The shoulder joint’s complex structure makes it particularly susceptible to various types of injuries and conditions. Modern medicine continues to advance treatment approaches, offering both traditional and cutting-edge therapies that address the underlying causes of shoulder discomfort while promoting healing and restoration of function. From non-invasive approaches to advanced surgical techniques, the medical field has developed numerous strategies to address shoulder pain effectively.
What Causes Shoulder Pain?
Shoulder pain stems from various sources, each requiring specific diagnostic and treatment approaches. Rotator cuff injuries represent one of the more common causes, occurring when the tendons and muscles that stabilize the shoulder joint. These damages may arise through overuse, acute trauma, or age-related wear. These injuries can range from minor inflammation to complete tears of the rotator cuff tendons.
Frozen shoulder develops when the shoulder capsule becomes inflamed and stiff, severely limiting its range of motion. This condition often progresses through distinct phases, beginning with pain and gradually transitioning to stiffness before eventual recovery. Arthritis can also affect the shoulder joint, with osteoarthritis causing cartilage breakdown and rheumatoid arthritis creating inflammatory damage. Shoulder instability, where the joint moves excessively or dislocates, can result from traumatic injuries or congenital factors affecting joint structure. Bursitis, inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs that cushion the shoulder joint, creates pain and swelling.
How Is the Source Diagnosed?
Accurate diagnosis forms the foundation of effective shoulder pain treatment. Medical professionals employ multiple assessment techniques to identify the specific cause and extent of shoulder problems. The diagnostic process typically begins with a comprehensive medical history and physical examination.
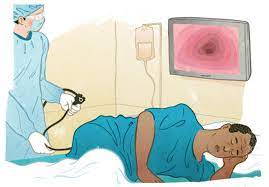
Imaging studies provide detailed views of shoulder structures. X-rays reveal bone abnormalities, fractures, and arthritic changes, while MRIs offer superior visualization of soft tissues, including muscles, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. Arthroscopy, a minimally invasive surgical procedure, allows direct visualization of internal shoulder structures when other diagnostic methods prove inconclusive. This procedure can serve both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, enabling physicians to identify problems and potentially treat them during the same session.
What Treatments Reduce the Pain?
Treatment approaches for shoulder pain have evolved significantly, incorporating both time-tested methods and innovative therapies. Non-surgical treatments often serve as the first line of intervention. Physical therapy remains a cornerstone of shoulder pain management, focusing on strengthening exercises, range of motion improvement, and movement pattern correction.
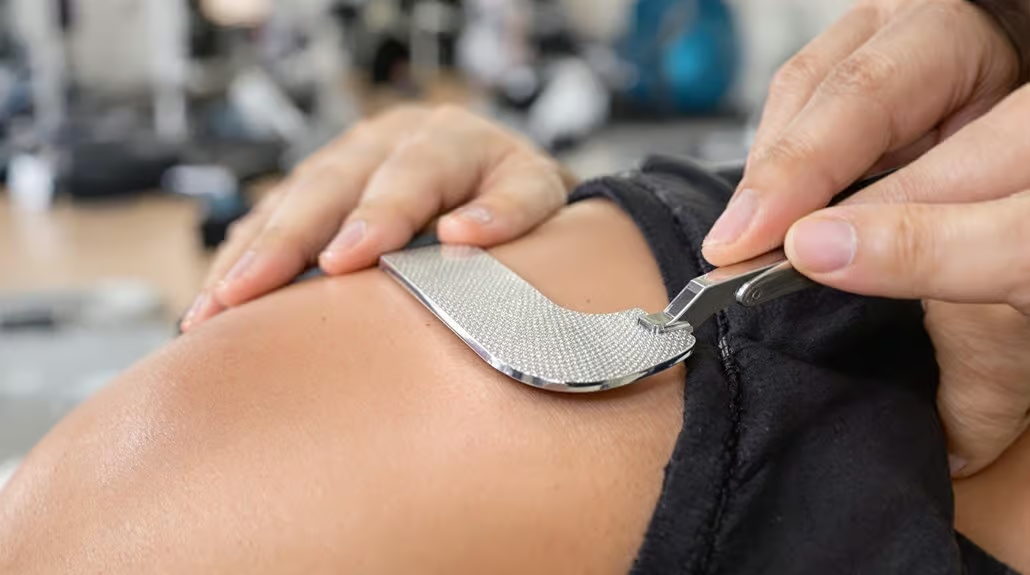
Regenerative medicine has introduced promising options, including platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, which uses concentrated platelets from the patient’s blood to promote healing. Stem cell therapy represents another frontier in shoulder treatment, potentially helping regenerate damaged tissues. Corticosteroid injections provide targeted pain relief and inflammation reduction. Surgical interventions range from minimally invasive arthroscopic procedures to open surgical repairs. Arthroscopic techniques allow surgeons to address rotator cuff tears and repair structural problems through small incisions. Non-invasive options for reducing inflammation and promoting tissue repair.
Consult an Orthopedic Expert
While some minor shoulder discomfort may resolve with rest and conservative measures, persistent or severe pain warrants professional medical evaluation. Orthopedic specialists possess the expertise and diagnostic tools necessary to accurately identify the source of shoulder problems and develop appropriate treatment plans. Early intervention often leads to better outcomes and may prevent minor issues from progressing to more serious conditions requiring extensive treatment. Professional evaluation becomes particularly valuable when pain persists beyond a few weeks, interferes with sleep, or limits normal activities.
- Pedrovazpaulo Wealth Investment: Unlocking Financial Freedom Through Innovative Strategies
- EO Pis: A Comprehensive Guide to Environmental Objectives and Performance Indicators
- Premiumindo69: The Future of Digital Entertainment
- Macadamia Nut Milk: Health Benefits, Recipes, and Why It’s the Perfect Dairy-Free Alternative
- Hentquz: The Future of Productivity and Collaboration