What is Non-Invasive Cardiology?
Non-invasive cardiology refers to medical tests and procedures that evaluate the heart without inserting instruments into the body. Unlike surgeries or catheter-based tests, these methods are safe, painless, and usually done in outpatient settings.
These procedures are designed to:
- Detect early signs of heart problems
- Monitor existing heart conditions
- Evaluate how well your heart is working
- Guide further treatment if needed
Why Non-Invasive Methods Are Important
Non-invasive cardiology offers many benefits, including:
- No recovery time needed
- Lower risk of complications
- Cost-effective compared to surgical procedures
- Useful for routine check-ups and long-term monitoring
It’s especially helpful for patients who aren’t ready for surgery or who have conditions that require regular observation.
Common Non-Invasive Cardiology Procedures
Let’s explore some of the most commonly used non-invasive heart tests:
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
- What it does: Measures the electrical activity of your heart.
- Why it’s used: To detect irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias), heart attacks, and other electrical issues.
- How it works: Small patches (electrodes) are placed on your chest, arms, and legs.
✅ Fast, painless, and gives immediate results.
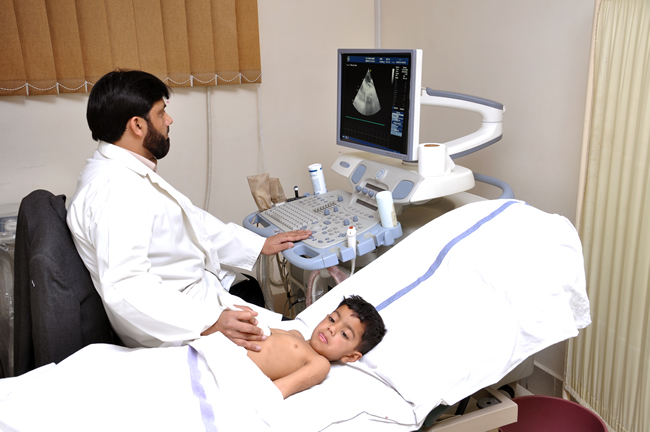
Echocardiogram
- What it does: Uses sound waves (ultrasound) to create pictures of your heart.
- Why it’s used: To check how well your heart is pumping, and to see the size, shape, and movement of heart structures.
- How it works: A device called a transducer is placed on your chest and moved around to capture images.
✅ Like an ultrasound for the heart – no needles, no surgery.
Stress Test (Exercise or Chemical)
- What it does: Shows how your heart performs under stress, usually during physical activity.
- Why it’s used: To identify coronary artery disease or other heart problems that may only appear during exertion.
- How it works: You walk on a treadmill while your heart activity is monitored. If you can’t exercise, medication is used to simulate stress.
✅ Reveals how your heart reacts to pressure.
4. Cardiac CT (Computed Tomography) Scan
- What it does: Creates detailed 3D images of your heart and blood vessels.
- Why it’s used: To detect plaque build-up, blockages, or other structural issues.
- How it works: You lie in a CT scanner while contrast dye may be injected to highlight your arteries.
✅ Quick and detailed imaging with minimal discomfort.
Cardiac MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
- What it does: Produces highly detailed images of your heart tissues.
- Why it’s used: To check for damage from heart attacks, inflammation, or heart muscle disease.
- How it works: You lie still in an MRI scanner while it takes pictures using magnetic fields and radio waves.
✅ Provides the most detailed pictures of the heart.
Holter Monitor
- What it does: Monitors your heart rhythm for 24 to 48 hours.
- Why it’s used: To detect irregular heartbeats that don’t occur during a brief ECG.
- How it works: You wear a small device connected to electrodes taped to your skin.
✅ Live with it for a day or two – it records your heart’s every beat.
When Are These Procedures Recommended?
Your doctor might recommend non-invasive cardiology tests if:
- You have symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, or palpitations.
- You have a family history of heart disease.
- You’ve already been diagnosed with a heart condition and need monitoring.
- You’re planning surgery and need your heart assessed beforehand.
How to Prepare for a Non-Invasive Test
Most of these procedures require little to no preparation, but here are a few tips:
- Wear comfortable clothing, especially for stress tests.
- Avoid caffeine and smoking before certain tests.
- Follow any fasting or medication instructions provided by your doctor.
What Happens After the Test?
Once your test is complete, a cardiologist will review the results. They may:
- Confirm your heart is healthy ✅
- Recommend lifestyle changes 🥗🚶
- Prescribe medications 💊
- Suggest further testing or treatment, if needed 🏥
The beauty of non-invasive cardiology is that it often provides all the information doctors need without surgery or invasive tools.
Prevention is Still Key
While these tests are great tools, keeping your heart healthy is even better. Focus on:
- Eating a heart-friendly diet
- Staying physically active
- Managing stress
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol
- Getting regular check-ups
Final Thoughts
Non-invasive cardiology procedures have revolutionized how we detect and manage heart disease. They’re safe, quick, and often the first step in understanding what’s going on inside your chest. If you or someone you love is concerned about heart health, don’t wait. Ask your doctor about these tests — they might just save a life.
FAQs About Non-Invasive Cardiology
1. Is an echocardiogram the same as an ECG?
No. An ECG records electrical activity, while an echocardiogram uses ultrasound to create heart images.
2. Are non-invasive tests painful?
Not at all. Most are completely painless and do not require needles or surgery.
3. How long does a stress test take?
A typical stress test takes about 30 to 45 minutes, depending on the method used.
4. Can these tests detect all heart problems?
They can detect many, but not all. Sometimes, more invasive procedures are needed for a complete diagnosis.
5. How often should I have these tests?
It depends on your risk factors, age, and symptoms. Always follow your cardiologist’s advice.